Individuals have looked for sex contrasts in human minds since at any rate the nineteenth century, when researcher Samuel George Morton emptied seeds and lead shot into human skulls to quantify their volumes.
Gustave Le Bon discovered men's minds are normally bigger than women's, which incited Alexander Bains and George Romanes to contend this size distinction makes men more intelligent. Be that as it may, John Stuart Plant brought up, by this basis, elephants and whales ought to be more brilliant than individuals.
So center moved to the general sizes of mind districts. Phrenologists recommended the piece of the cerebrum over the eyes, called the frontal flap, is generally significant for insight and is relatively bigger in men, while the parietal projection, simply behind the frontal projection, is relatively bigger in ladies. Afterward, neuroanatomists contended rather the parietal flap is more significant for insight and men's are really bigger.
In the twentieth and 21st hundreds of years, scientists searched for unmistakably female or male attributes in littler mind developments. As a conduct neurobiologist and creator, I think this hunt is confused in light of the fact that human cerebrums are so changed.
Anatomical cerebrum contrasts
The biggest and most predictable mind sex distinction has been found in the nerve center, a little structure that manages conceptive physiology and conduct. At any rate one hypothalamic region is bigger in male rodents and people.
Be that as it may, the objective for some, specialists was to distinguish mind reasons for assumed sex contrasts in intuition – not simply conceptive physiology – thus consideration went to the huge human cerebrum, which is liable for knowledge.
Inside the cerebrum, no district has gotten more consideration in both race and sex distinction research than the corpus callosum, a thick band of nerve filaments that conveys signals between the two cerebral sides of the equator.
In the twentieth and 21st hundreds of years, a few scientists found the entire corpus callosum is relatively bigger in ladies all things considered while others discovered just certain parts are greater. This distinction drew well known consideration and was recommended to cause intellectual sex contrasts.
Be that as it may, littler minds have a relatively bigger corpus callosum paying little mind to the proprietor's sex, and investigations of this present structure's size contrasts have been conflicting. The story is comparable for other cerebral measures, which is the reason attempting to clarify assumed psychological sex contrasts through cerebrum life structures has not been productive.
Female and male qualities commonly cover
In any event, when a mind area shows a sex distinction by and large, there is ordinarily significant cover between the male and female disseminations. On the off chance that a characteristic's estimation is in the covering area, one can't foresee the individual's sex with certainty.
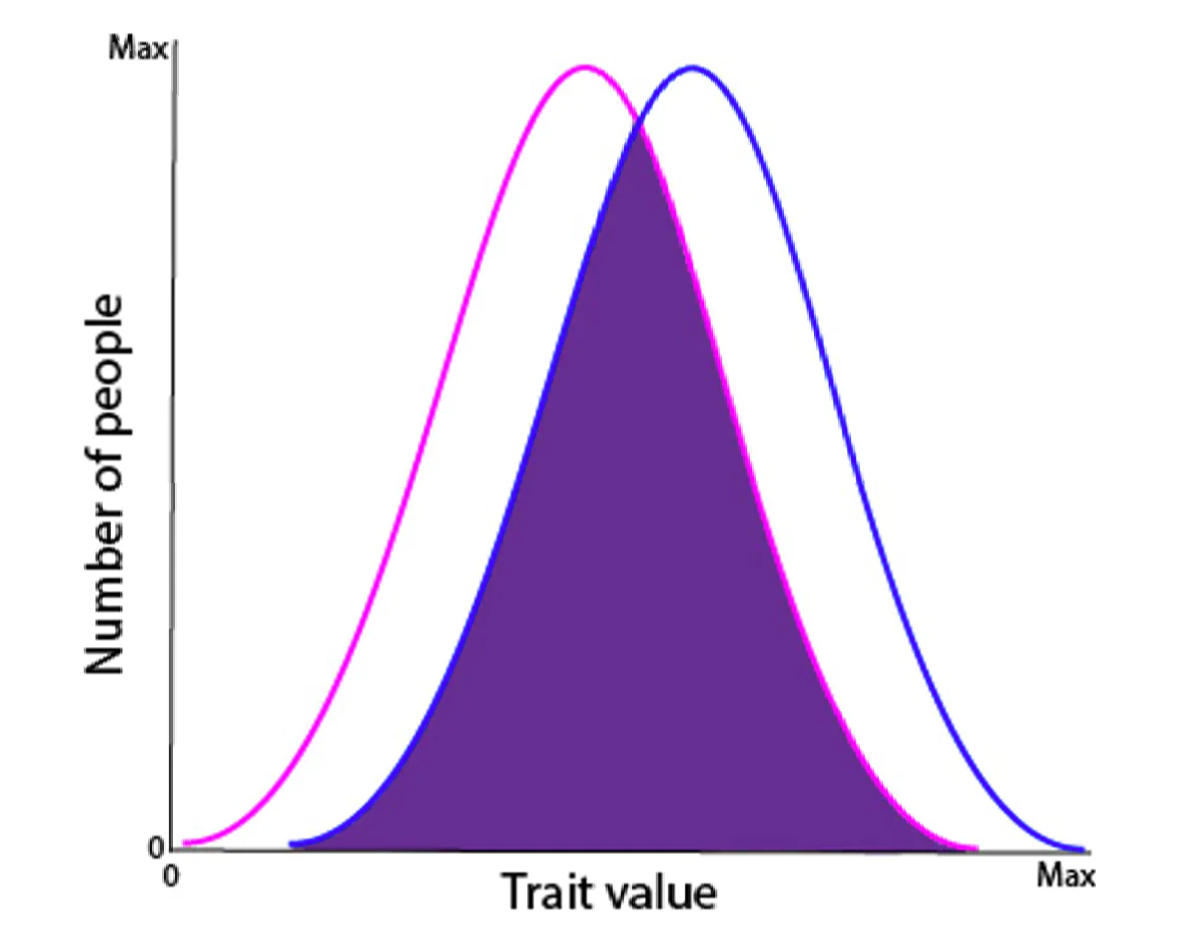 Chart shows how measurements that differ between sexes (f = pink, m = blue) also overlap. (Ari Berkowitz, CC BY)
Chart shows how measurements that differ between sexes (f = pink, m = blue) also overlap. (Ari Berkowitz, CC BY)For instance, consider tallness. I am 5'7". Does that disclose to you my sex? Furthermore, cerebrum districts normally show a lot littler normal sex contrasts than tallness does.
Neuroscientist Daphna Joel and her partners inspected X-rays of more than 1,400 minds, estimating the 10 human cerebrum districts with the biggest normal sex contrasts.
They surveyed whether every estimation in every individual was toward the female finish of the range, close to the male end or halfway. They found that solitary 3 percent to 6 percent of individuals were reliably "female" or "male" for all structures. Every other person was a mosaic.
Pre-birth hormones
When mind sex contrasts do happen, what causes them?
A recent report originally exhibited that an infusion of testosterone into a pregnant rat makes her female posterity show male sexual practices as grown-ups.
The creators derived that pre-birth testosterone (ordinarily emitted by the fetal testicles) for all time "arranges" the mind. Numerous later examinations demonstrated this to be basically right, however distorted for nonhumans.
Specialists can't morally adjust human pre-birth hormone levels, so they depend on "incidental tests" in which pre-birth hormone levels or reactions to them were irregular, for example, with intersex individuals.
Be that as it may, hormonal and ecological impacts are entrapped in these examinations, and discoveries of mind sex contrasts have been conflicting, leaving researchers without clear ends for people.
Qualities cause some cerebrum sex contrasts
While pre-birth hormones presumably cause most cerebrum sex contrasts in nonhumans, there are a few situations where the reason is legitimately hereditary.
This was significantly appeared by a zebra finch with an abnormal peculiarity – it was male on its correct side and female to its left side. A singing-related cerebrum structure was extended (as in regular guys) just on the right, however the different sides encountered the equivalent hormonal condition.
Therefore, its cerebrum asymmetry was not brought about by hormones, however by qualities straightforwardly. From that point forward, direct impacts of qualities on cerebrum sex contrasts have likewise been found in mice.
Learning changes the mind
Numerous individuals accept human cerebrum sex contrasts are intrinsic, yet this supposition that is confused.
People adapt rapidly in adolescence and keep learning – oh dear, more gradually – as grown-ups. From recollecting realities or discussions to improving melodic or athletic abilities, learning modifies associations between nerve cells called neural connections. These progressions are various and visit however normally tiny – short of what one hundredth of the width of a human hair.
Investigations of a bizarre calling, in any case, show learning can change grown-up minds drastically. London cab drivers are required to remember "the Information" – the intricate courses, streets and tourist spots of their city.
Scientists found this adapting genuinely changed a driver's hippocampus, a mind locale basic for route. London cabbies' back hippocampi were seen as bigger than nondrivers by millimeters – in excess of multiple times the size of neurotransmitters.
So it's not sensible to expect any human mind sex contrasts are intrinsic. They may likewise come about because of learning. Individuals live in an on a very basic level gendered culture, in which child rearing, training, desires and openings contrast dependent on sex, from birth through adulthood, which definitely changes the mind.
Eventually, any sex contrasts in mind structures are no doubt because of a complex and associating blend of qualities, hormones and learning.The Discussion
Ari Berkowitz, Presidential Educator of Science; Chief, Cell and Conduct Neurobiology Graduate Program, College of Oklahoma.






No comments:
Post a Comment