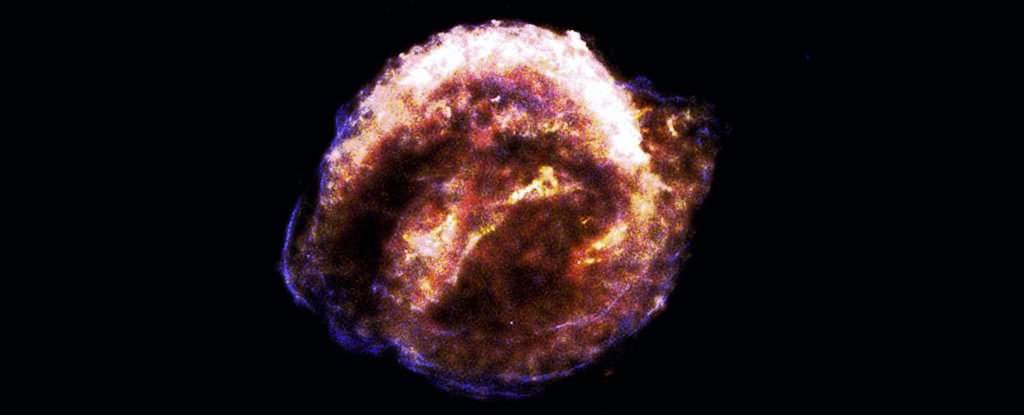
Toward the finish of the Universe, long after the last sparkling stars flash out, there may be one last arrangement of blasts. Called dark smaller person supernovae, these amazing impacts will proclaim in the never-ending murkiness as the Universe sinks into torpidity, another examination proposes.
These recently proposed supernovas are a unique variety that haven't yet happened anyplace Known to man. Dark bantam supernovas may be the last occasions that occur Known to mankind, which by then will be a to a great extent void spot where the temperature approaches outright zero.
Stars' lives and passings are controlled by their mass. Huge ones 10 or more occasions the mass of the sun detonate as supernovas and can become dark openings.
However, littler ones, which don't create heavier components through the atomic combination at their centers, end their lives as little thick husks of stars known as white diminutive people. More than trillions of years, they diminish and transform into solidified, dark articles known as dark midgets.
Another paper, to be distributed in the diary Month to month Notification of the Illustrious Galactic Culture, portrays how these dark midgets may at last delivery the last pieces of light Known to man as they detonate as supernovas.
The dark bantam supernovas would frame through a quantum cycle known as pycnonuclear combination. Stars are regularly energized by nuclear combination, where high temperatures and weights defeat nuclear cores' normal electric repugnance, permitting iotas to meld into new, heavier components.
However, in pycnonuclear combination, quantum burrowing permits nuclear cores to draw nearer to one another than they typically would. Pycnonuclear combination can in this manner gradually transform the components in the white midget into iron – the last component that can be made by combination.
"These responses take a madly prolonged stretch of time," said study creator Matt Caplan, hypothetical physicist at Illinois State College. "You could hold up a million years and not see a solitary combination response in a dark smaller person."
By examination, the Sun intertwines more than 10^38 protons every second. To change over a dark smaller person into iron by pycnonuclear combination would take an amazing 10^1,100 and 10 ^32,000 years. In the event that you worked out all the zeros in these numbers, they'd take up the length of a passage to an entire book part, individually.
"These time scales are tremendous," said Fred Adams, astrophysicist at the College of Michigan, who was not engaged with the new examination.
"We expect the biggest conceivable dark gaps to be vanished on time sizes of just around 10 to the 100 years, which is prompt contrasted with the occasions examined in the paper."
When the dark diminutive person was generally iron, it would be squashed by its own mass. This runaway breakdown – the supernova – would trigger an enormous collapse that launches the external layers of the extra dark smaller person.
In bigger stars today, this iron accident is likewise what prompts the more normal supposed center breakdown supernovas.
Dark smaller person supernovae, in any case, would just happen in dark small stars with masses somewhere in the range of 1.16 and 1.35 occasions that of the Sun. Those dark small stars are thusly made from common stars that start off with six to multiple times the mass of the Sun.
"[It] isn't actually an uncommon populace, yet in addition not the most widely recognized," Caplan said.
Truth be told, these stars make up around 1 percent of all stars today, and Caplan gauges there will be around a billion trillion (10^21) of these supernovae before the finish of the Universe.
Since the dark diminutive people have genuinely low masses, the dark bantam supernovas would presumably be somewhat littler than ones happening in the current Universe, yet dynamite in an in any case totally dark Universe.
After these last pants of light, nothing left Known to man will have the option to detonate or sparkle.
So while the Universe will apparently end in ice, there will be a sparkle of fire en route.

Toward the finish of the Universe, long after the last sparkling stars flash out, there may be one last arrangement of blasts. Called dark smaller person supernovae, these amazing impacts will proclaim in the never-ending murkiness as the Universe sinks into torpidity, another examination proposes.
These recently proposed supernovas are a unique variety that haven't yet happened anyplace Known to man. Dark bantam supernovas may be the last occasions that occur Known to mankind, which by then will be a to a great extent void spot where the temperature approaches outright zero.
Stars' lives and passings are controlled by their mass. Huge ones 10 or more occasions the mass of the sun detonate as supernovas and can become dark openings.
However, littler ones, which don't create heavier components through the atomic combination at their centers, end their lives as little thick husks of stars known as white diminutive people. More than trillions of years, they diminish and transform into solidified, dark articles known as dark midgets.
Another paper, to be distributed in the diary Month to month Notification of the Illustrious Galactic Culture, portrays how these dark midgets may at last delivery the last pieces of light Known to man as they detonate as supernovas.
The dark bantam supernovas would frame through a quantum cycle known as pycnonuclear combination. Stars are regularly energized by nuclear combination, where high temperatures and weights defeat nuclear cores' normal electric repugnance, permitting iotas to meld into new, heavier components.
However, in pycnonuclear combination, quantum burrowing permits nuclear cores to draw nearer to one another than they typically would. Pycnonuclear combination can in this manner gradually transform the components in the white midget into iron – the last component that can be made by combination.
"These responses take a madly prolonged stretch of time," said study creator Matt Caplan, hypothetical physicist at Illinois State College. "You could hold up a million years and not see a solitary combination response in a dark smaller person."
By examination, the Sun intertwines more than 10^38 protons every second. To change over a dark smaller person into iron by pycnonuclear combination would take an amazing 10^1,100 and 10 ^32,000 years. In the event that you worked out all the zeros in these numbers, they'd take up the length of a passage to an entire book part, individually.
"These time scales are tremendous," said Fred Adams, astrophysicist at the College of Michigan, who was not engaged with the new examination.
"We expect the biggest conceivable dark gaps to be vanished on time sizes of just around 10 to the 100 years, which is prompt contrasted with the occasions examined in the paper."
When the dark diminutive person was generally iron, it would be squashed by its own mass. This runaway breakdown – the supernova – would trigger an enormous collapse that launches the external layers of the extra dark smaller person.
In bigger stars today, this iron accident is likewise what prompts the more normal supposed center breakdown supernovas.
Dark smaller person supernovae, in any case, would just happen in dark small stars with masses somewhere in the range of 1.16 and 1.35 occasions that of the Sun. Those dark small stars are thusly made from common stars that start off with six to multiple times the mass of the Sun.
"[It] isn't actually an uncommon populace, yet in addition not the most widely recognized," Caplan said.
Truth be told, these stars make up around 1 percent of all stars today, and Caplan gauges there will be around a billion trillion (10^21) of these supernovae before the finish of the Universe.
Since the dark diminutive people have genuinely low masses, the dark bantam supernovas would presumably be somewhat littler than ones happening in the current Universe, yet dynamite in an in any case totally dark Universe.
After these last pants of light, nothing left Known to man will have the option to detonate or sparkle.
So while the Universe will apparently end in ice, there will be a sparkle of fire en route.







No comments:
Post a Comment